Recently, China’s Ministry of Emergency Management released the *Construction Standards for “Industrial Internet + Hazardous Chemical Safety Production” – Part 2: Special Work Permit Approval and Process Management (Draft for Comments) *. This has sparked widespread attention to special work permit systems in hazardous chemical enterprises.
In practice, we’ve observed a common misconception even among safety managers in hazardous chemical enterprises: they believe electronic work permit systems are merely digitized versions of paper permits. However, a closer look at the standards reveals a deeper reality. A truly effective electronic work permit system—one that meets essential safety control requirements and delivers seamless usability for frontline workers—aligns closely with the renowned “Iceberg Theory.”

Beneath its surface functionalities, a robust electronic work permit system must possess the following critical yet often overlooked capabilities:
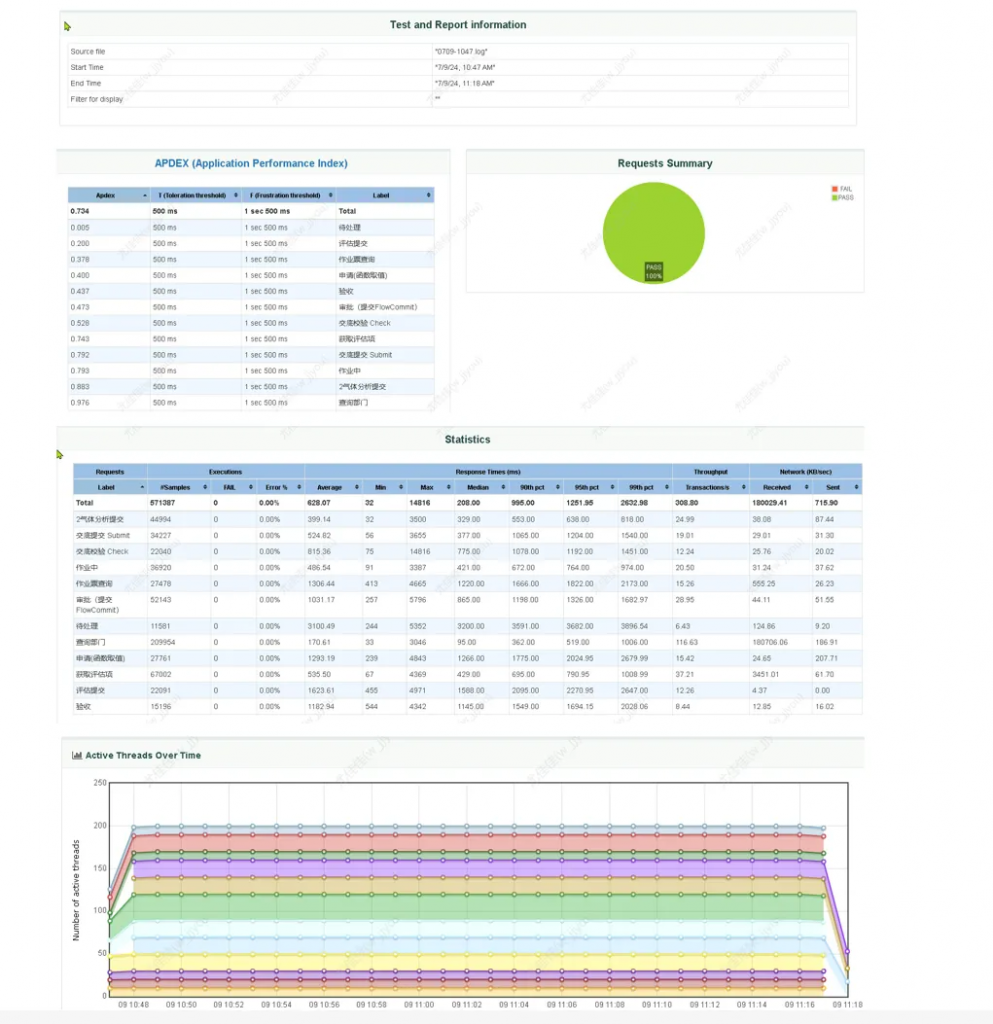
1.High Concurrency Performance
A distinctive feature of special operations in chemical plants (especially large-scale facilities) is the concentration of permit applications, evaluations, and approvals within the first 1–2 hours of morning and afternoon shifts. During these peak periods, thousands of employees may simultaneously use mobile apps or PCs to submit, review, approve, or query permits. These operations involve complex logical interconnections and require real-time data synchronization. For example, during routine production peaks, large plants may see thousands of concurrent users, while maintenance periods can surge to tens of thousands. Notably, most successful cases of 100% electronic work permit adoption during large-scale maintenance in the industry belong to In-Road Smart System users. Such high-concurrency capabilities are the result of In-Road’s decades of iterative optimization and technological refinement.
2.Intelligence and Adaptability
For chemical enterprises with stringent safety requirements, special operations demand extensive professional safety assessments and verification of control measures. This necessitates an electronic work permit system with full-process intelligence and adaptive capabilities. For instance:
・The system provides smart recommendations and constraints during safety evaluations based on selected work types, operational zones, or plant-specific processes.
・It automatically transfers workflows and responsibilities during personnel changes or shift handovers.
・Customizable configurations allow plants to align with national, regional, or corporate data standards while accommodating unique requirements.
・In-Road’s system incorporates over a dozen such intelligent and adaptive features, each requiring meticulous design and rigorous testing to ensure reliability.
4.Intuitive Interaction and Native-Level User Experience
Electronic work permit systems are primarily used in dynamic field environments, where user experience is critical. Workers need to operate the system swiftly and accurately to maintain safety and efficiency. Overly complex interfaces risk becoming burdensome. In-Road has invested heavily in its mobile app, tailoring interactions to frontline workflows:
・Visual Design: Clear, fatigue-resistant color schemes and intuitive UI components simplify permit creation and process tracking.
・Offline Functionality: Native app caching ensures uninterrupted operations even in areas with poor connectivity.
・Performance Optimization: Unlike cost-effective H5 apps, In-Road’s native development prioritizes responsiveness and adaptability to harsh field conditions.
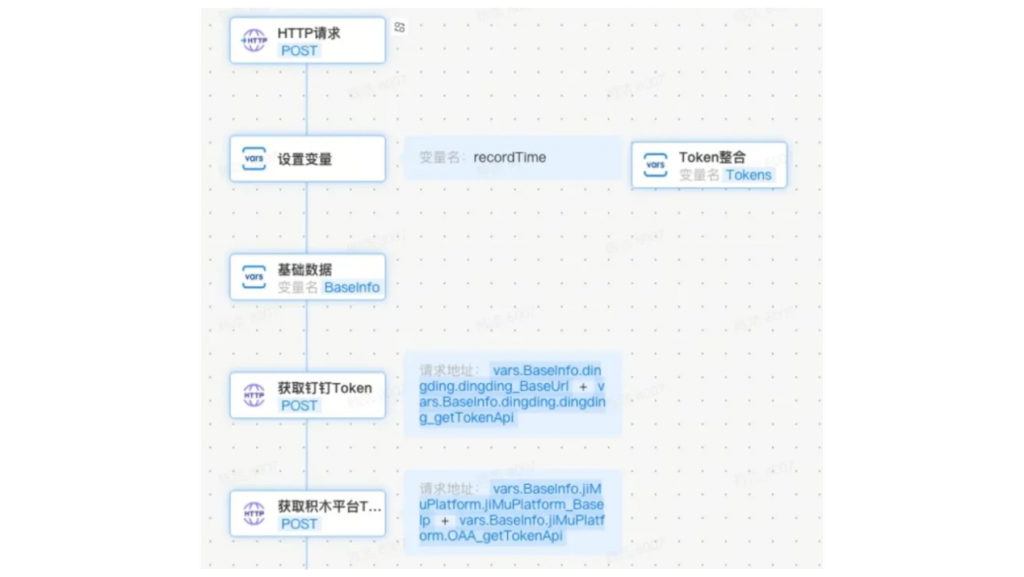
5.Flexible and Scalable Integration Capabilities
Special operations often intersect with multiple business systems. As safety regulations evolve and new technologies emerge, seamless integration becomes essential. For example:
・Location Tracking: Integration with personnel positioning systems triggers alerts for unauthorized zone breaches.
・AI Video Monitoring: Real-time detection of fire, smoke, or unsafe behaviors via AI systems.
・Access Control: Automated permit validation with electronic gate systems.
・Training Compliance: Linking with safety training platforms to ensure only certified personnel receive permits.
・However, integrating disparate systems from multiple vendors poses technical challenges. In-Road’s unified integration framework simplifies this process, whereas weaker vendors often impose high costs or abandon such efforts entirely.
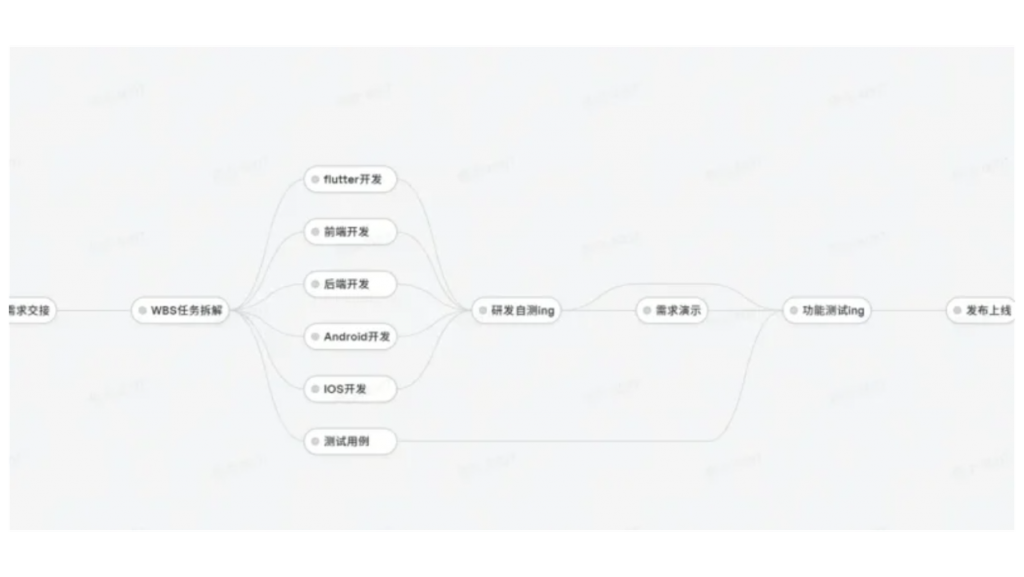
6.Professional R&D Process Management
In-Road employs advanced project management tools to oversee its development lifecycle—from requirements analysis and design to coding, testing, and deployment. This ensures rigorous quality control, resource optimization, and continuous improvement through data-driven insights.
In conclusion, developing a truly “effective” electronic work permit system for hazardous chemical enterprises is no simple task. By embedding complex functionalities beneath the “iceberg’s surface,” In-Road empowers frontline users to manage special operations safely and efficiently, fortifying safety defenses and driving operational excellence in the industry.










